DISGENET v25.2 brings enhanced clinical and molecular annotations designed to advance variant interpretation, disease modeling, and drug discovery workflows through more granular, actionable data.
Built for Biotech, Pharma, Translational R&D, and Clinical Genomics, v25.2 enables you to filter, score, and prioritize gene- and variant-disease associations with even deeper contextual data.
DISGENET version 25.2 includes:
- Smarter NLP Pipeline for Better Data
- Inheritance Mode for Mendelian Disorders
- Disease Prevalence
- Drug Modality Classification
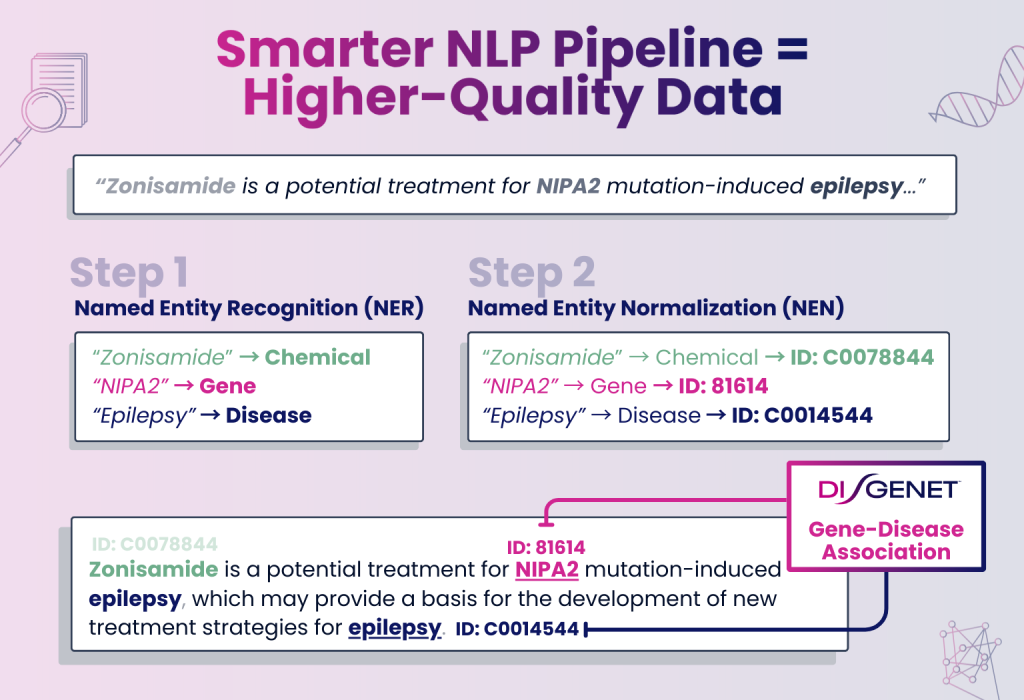
Smarter NLP Pipeline for Better Data
We know how critical data quality is to your work. That’s why DISGENET v25.2 features major improvements in our NLP pipeline, including new Named Entity Recognition (NER) and Named Entity Normalization (NEN) modules.
These updates deliver better extraction and mapping of diseases, genes, and chemicals from scientific literature — ensuring you have the most current and reliable data available.
Why Our Smarter NLP Matters to You
- Even more accurate extraction and mapping of diseases, genes, and chemicals from the latest scientific literature
- Improved concept normalization gives you deeper context, supporting better decision-making
- Leverage higher-quality association data for downstream applications, from target and biomarker discovery to drug repurposing and variant interpretation
This update results in an updated NER module with an average F1 score of 0.88, matching state-of-the-art performance and giving you deeper, more precise, and more reliable associations for your research.
Inheritance Mode for Mendelian Disorders
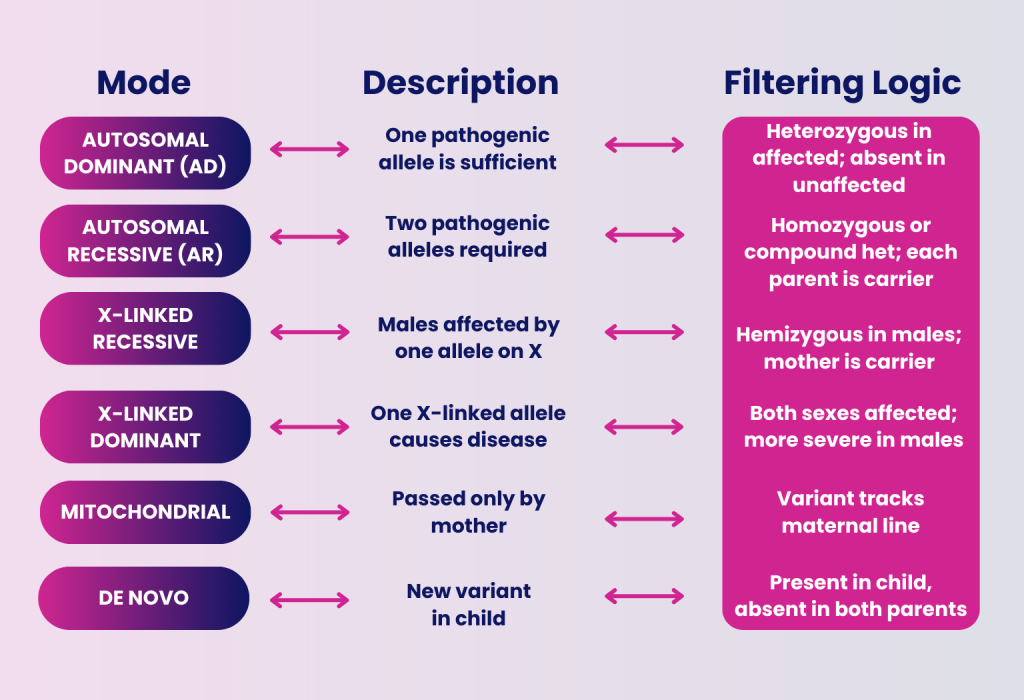
DISGENET v25.2 now includes information about mode of inheritance across 10 categories, including autosomal dominant, mitochondrial, oligogenic, multigenic disorders, and more.
How This Supports Your Work
In Clinical Genomics
- Guides variant filtering and prioritization by aligning expected zygosity (e.g., heterozygous, homozygous, hemizygous) with known inheritance patterns
- Increases diagnostic accuracy with inheritance-aware analyses such as segregation testing and de novo variant detection
- Reduces false positives and missed diagnoses in rare and complex conditions
In Drug R&D
- Informs therapeutic strategy by aligning treatment modalities with disease mechanisms:
- Recessive disorders may require gene replacement or enzyme supplementation
- Dominant disorders may benefit from allele-specific silencing, protein inhibition, or dominant-negative correction
- X-linked or mitochondrial disorders may suggest sex-specific or maternal-lineage-targeted approaches
- Recessive disorders may require gene replacement or enzyme supplementation
- Guides patient stratification and clinical trial design, identifying likely carriers, affected individuals, and at-risk relatives.
Disease Prevalence
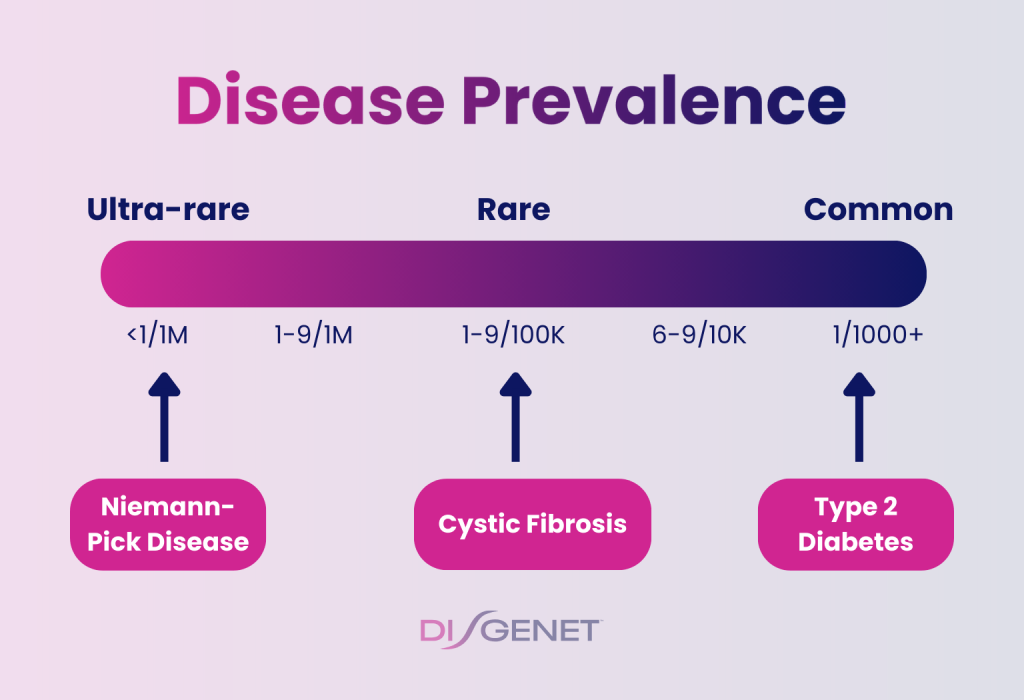
DISGENET v25.2 introduces disease prevalence annotations, including:
- Standardized prevalence bins (e.g., 1–9/100k, <1/1M)
- Geographic regions (Europe, North America, Asia, etc.)
- Method used to quantify prevalence depending on the timeframe and population context (point prevalence, prevalence at birth, lifelong prevalence, etc.)
How DISGENET Prevalence Supports You
In Clinical Genomics
- Informs allele frequency thresholds by helping define the maximum plausible frequency of pathogenic variants in population databases, especially for rare diseases.
- Supports pathogenicity assessment by contextualizing the likelihood that a variant observed in healthy individuals is compatible with disease prevalence, penetrance, and expressivity.
In Drug R&D
- Assesses market potential and ROI
- Prevalence data are essential for estimating patient population size, market viability, and cost-effectiveness — especially in orphan drug development.
- Informs regulatory strategy and incentives
- Diseases below certain prevalence thresholds may qualify for orphan drug designation, which provides financial and regulatory incentives (e.g., FDA, EMA).
- Affects trial feasibility and geographic targeting
- Knowledge of disease prevalence across populations supports decisions on trial site selection, epidemiological surveillance, and post-market planning.
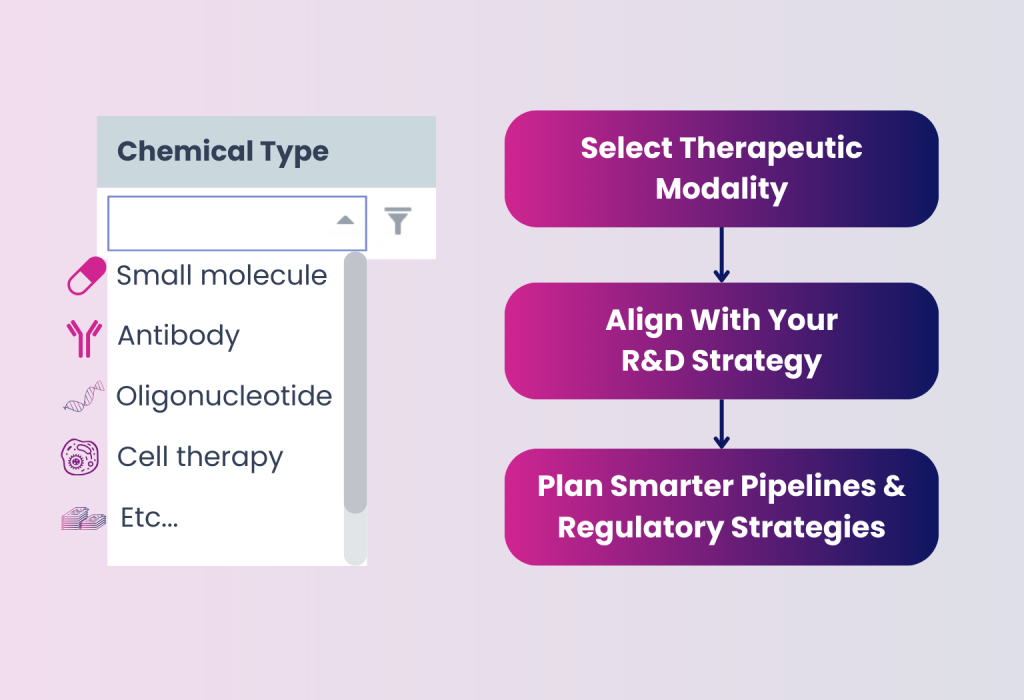
Drug Modality Classification
DISGENET now includes classifications of therapeutic molecule types, from small molecules and antibodies to oligonucleotides, gene therapies, cell therapies, and more.
How You Can Apply This
- Align target selection with your modality-specific R&D approach
- Improve pipeline planning and prioritization by molecule class
- Facilitate partner evaluation by highlighting modality fit
Get Started with DISGENET v25.2
Want to see how DISGENET fits your pipeline?